If you suffer from chronic neck pain, the source of your discomfort may be a herniated cervical disc. Here, we'll discuss cervical herniated disc symptoms, the causes and the treatment options available to correct this condition.
What Is a Vertebral Disc?
Vertebral discs are found in between the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae. They play a vital role in protecting the bones from injury, providing cushion and support, allowing flexibility, and helping to disperse the load placed on vertebral bodies.
The discs are composed of a tough, fibrous outer ring, called the annulus fibrosus, and a softer inner core, known as the nucleus pulposus. In cervical discs, the collagen fibers of the outer ring help distribute the weight of the head, while the gel-like inner core acts as a shock absorber, protecting against compressive trauma to the vertebrae.
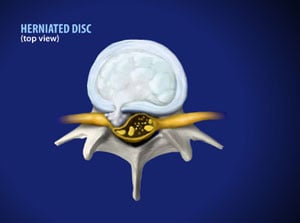 Why Do Discs Herniate?
Why Do Discs Herniate?
Disc herniation can result from natural, degenerative changes that take place as we age. It can also occur secondary to traumatic injury. The disc can leak fluid, which places pressure on surrounding nerves, causing the symptoms we typically associate with herniation: numbness and tingling down the arms, pain, and loss of function. Taken together, these symptoms constitute a condition called cervical radiculopathy.
How Do Doctors Diagnose a Herniated Disc?
There are several diagnostic imaging tests your doctor can perform to determine if you are suffering from a cervical herniated disc. They include:
- MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging is the preferred diagnostic test for disc herniation. MRI uses high-powered magnetic fields and radiofrequency pulses to obtain detailed images of soft tissue, bones, and organs, and can capture potentially damaged nerve ends associated with herniation.
- CT with myelogram: Computerized tomography (CT), combined with a myelogram, is another type of detailed imaging. A dye is injected into the affected area, highlighting the damaged nerve root, and recorded via the CT scan. This test poses an added risk, because the dye must be injected into the spinal canal. It is also more expensive.
Are There Conservative Treatments for Cervical Herniated Disc?
Several conservative treatments for cervical herniation can be undertaken before considering a surgical option. These include:
- Pain management, steroids, and anti-inflammatory drugs, which can alleviate the discomfort while reducing inflammation of the affected nerve
- Traction, in which a cervical device is used to alleviate pressure on the affected nerve by applying upward pressure to the neck
- Physical therapy, during which a licensed therapist instructs the patient in exercises to alleviate arm pain and strengthen muscles; educates the patient in ways to avoid further injury; and sometimes uses hot/cold therapy to help reduce pain, symptoms, and inflammation
- Manual manipulation, which is performed by an osteopathic or chiropractic professional who gently manipulates the cervical spine to reduce joint dysfunction and restore mobility
What Are My Surgical Options?
If conservative treatments fail to alleviate your pain and symptoms, your doctor will probably recommend a surgical alternative to correct the herniated disc. There are generally two procedures used to correct cervical herniation:
- ACDF: Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) is a common means of correcting cervical disc herniation. The surgeon makes a small incision in the front (anterior) of the neck, then removes the affected disc. The vertebrae above and below are then fused, using a metal plate and screws. While this procedure effectively stabilizes the joint, mobility is lost once the bones are fused.
- ACDR: Artificial cervical disc replacement (ACDR) uses the same anterior approach to removing the affected disc, but instead of fusing the bones together, the damaged disc is replaced with a graft. The source of the graft may be the patient (an autograft), a donor or tissue bank (an allograft), or a commercial, synthetic replacement. The graft will mimic the original disc, providing cushion and support for the cervical joint while maintaining mobility.
- PDR: Posterior disc replacement (PDR) is similar to ACDR, only the incision is made in the back (posterior) of the neck. The main drawbacks of PDR are the potential for bleeding due to disruption of surrounding vessels and added manipulation of the spinal cord.
What Is Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery?
When deciding on a surgical treatment for your cervical herniated disc, be sure to choose a surgeon who offers a minimally invasive approach. Minimally invasive spine surgery (MISS) provides a superior technique compared to conventional spinal surgery. Utilizing small incisions and aided by high-powered microscopes, surgeons trained in MISS can offer a range of advantages, including:
- Less trauma to surrounding tissues, which means less blood loss for the patient
- A faster recovery, with less scarring and pain
- A speedy turnaround, because the procedures are performed on an outpatient basis
- Less risk of hospital-based infection when performed at a specialized surgical center
Make sure your surgeon is board certified, which ensures that they have the appropriate education, training, and experience in spinal surgery. And choose a surgeon with a proven track record of successful MISS and who works within an integrated center that can oversee your care from initial diagnosis to recovery. There's no need to go with conventional surgery when MISS offers a far superior approach to cervical herniated disc treatment.

About the author
Robert S. Bray, Jr., M.D. Nicknamed “Dr. Fix-It” by The Red Bulletin, Robert S. Bray, Jr., M.D. makes an art of helping the world’s most elite athletes return to push the boundaries of performance. The neurological spine surgeon, recognized globally for his thorough diagnoses and pioneering minimally invasive approach, is quickly redefining sports medicine, one champion at a time. Dr. Bray founded the state-of-the-art, multi-disciplinary DISC Sports & Spine Center (DISC) in 2006 located in Los Angeles, CA. Read more articles by Robert S. Bray, Jr., M.D..





